红外与激光工程
2021, 50(7): 20211053
1 中国科学院空间光电精密测量技术重点实验室, 成都 610209
2 电子科技大学 光电科学与工程学院, 成都 611731
3 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 成都 610209
4 空军装备部驻成都地区第五军事代表室, 成都 610000
针对偏振三维成像系统的高效目标三维点云分割问题, 提出一种多维信息融合的高效分割理念。系统采用高分辨率EMCCD相机作为面阵探测器, 在一次成像过程中, 可同时获得视场中的灰度图像以及三维点云数据。根据该成像特点, 建立灰度图的像素坐标与点云数据像素坐标之间的点对点映射关系, 结合粒子群优化算法的边缘分割方法, 将灰度图中目标分割后的坐标信息映射到三维点云数据中, 得到其三维点云数据。该方法将三维点云数据降维处理为二维图像处理, 显著降低了计算复杂度, 避免了点云数据误差对分割精度造成的影响。实验验证了多维数据融合目标三维点云分割方法的有效性。
面阵激光雷达 偏振调制 数据融合 粒子群优化算法 点云分割 planar lidar polarization-modulation data fusion particle swarm optimization algorithm point cloud segmentation
1 中国科学院 空天信息创新研究院, 北京 100094
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3 中国科学院 电子学研究所, 北京 100190
为满足合成孔径雷达实时成像、数据回放等高速可靠数据传输需求, 解决传统数据传输系统由于接口要求高、体积与功耗大以及网络配置不灵活等原因不适合用于外场试验的问题, 基于ZYNQ芯片设计一种光纤接口到以太网接口的数据传输系统。主要介绍数据传输流程的实现方法, 并提出一种三级乒乓和指令并行的优化策略保证数据正确, 提高传输速度; 通过移植嵌入式Linux系统实现灵活修改网络配置。与传统方案相比, 该系统在体积、功耗和灵活性上具有明显优势。经实验验证, 数据传输速度可达770 Mb/s。
高速数据传输 合成孔径雷达 Aurora IP用户接口 千兆以太网 现场可编程门阵列 嵌入式Linux 内存映射 乒乓操作 high-speed data transmission synthetic aperture radar Aurora IP user interface gigabit ethernet field programmable gate array embedded Linux memory mapping ping-pong operation
1 中国科学院空间光电精密测量技术重点实验室, 成都 610209
2 电子科技大学 光电科学与工程学院, 成都 610054
3 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 成都 610209
4 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
提出一种基于新型成像传感器——电子倍增电荷耦合器件的超分辨率偏振调制三维成像系统。利用低带宽电光调制器作为亚纳秒级高速快门, 实现三维成像系统时间(距离)分辨能力。该系统只需要采集一帧原始数据, 就可以从灰度图像中重建深度信息, 实现动态成像。基于该系统结构提出多维数据融合求解目标位姿的方法, 并通过试验验证了方法的可行性。实验结果表明, 对距离激光雷达1km外的目标进行测量, 其位移精度小于3cm, 位姿角误差小于3°。
激光雷达 时间分辨成像 偏振调制 多维数据融合 姿态估计 lidar time resolved imaging polarization modulation multidimensional data fusion pose estimation
许振兴 1,2,3,4杨平 1,3,4,*程涛 1,3,4许冰 1,3,4李和平 2
1 中国科学院光电技术研究所自适应光学重点实验室, 四川 成都 610209
2 电子科技大学光电科学与工程学院, 四川 成都 610054
3 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 四川 成都 610209
4 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
提出了基于远场指标梯度的自适应光学闭环控制模型,该模型使用递归最小二乘来稳定响应矩阵,通过远场指标的梯度信息快速自学习当前的系统状态。结果表明:该模型具有在线实时更新的特点,能够自适应H-S子孔径缺光或质心探测不理想的状态,可在一定程度上改善控制性能。
自适应光学 递归最小二乘 波前复原 远场指标 许振兴 1,2,3,4,**杨平 1,3,4,*程涛 1,3,4许冰 1,3,4李和平 2
1 中国科学院光电技术研究所自适应光学重点实验室, 四川 成都 610209
2 电子科技大学光电科学与工程学院, 四川 成都 610054
3 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 四川 成都 610209
4 中国科学院大学, 北京 100039
在自适应光学系统中,传统比例-积分控制模型依赖于变形镜的响应矩阵,系统状态的改变会对变形镜响应矩阵造成影响,导致波前校正性能下降。通过重新定义BP(back-propagation)神经网络结构实现哈特曼斜率数据到控制信号的输出,并建立了控制模型。实验结果表明,所提模型摆脱了传统固定模型的限制,具有在线更新控制模型的特点,控制模型收敛性能良好,能适应系统状态变化,有较强的鲁棒性,同时提高了控制精度,一定程度上改善了控制性能。
自适应光学 神经网络 响应矩阵 波前校正
1 空军军医大学军事预防医学系辐射防护医学教研室, 陕西 西安 710032
2 清华大学工程物理系, 北京 100084
3 华北理工大学机械工程学院, 河北 唐山 063500
人脐带间充质干细胞(hUC-MSCs)是一种具有多向分化潜能的干细胞, 具有广阔的应用前景, 但是由于其体外大量增殖和定向分化等问题尚未解决, 制约了其进一步应用。既往研究表明, 大气压冷等离子体(CAP)可促进离体培养的脂肪或骨髓来源MSCs的增殖和分化, 但对hUC-MSCs的影响国内外尚未见报道。因此, 本研究的目标是探讨CAP对hUC-MSCs增殖和成骨分化的影响。在电源频率(17 kHz)和气体流量(4 slpm)保持不变的条件下, 原代培养的hUC-MSCs经不同放电电压下产生的氦(He)等离子体处理后, 在不同时间点收集细胞, 采用CCK-8法检测细胞活力, 微板法检测碱性磷酸酶(ALP)的活性, 茜红素染色检测钙化结节的形成。结果显示, 与对照组相比, 纯氦气组上述指标无明显变化, 而CAP组的细胞活力显著降低, 并且与等离子体放电电压和处理时间呈负相关;CAP处理10 s和30 s后, ALP活性则无明显变化, 而处理60 s后ALP活性显著下降, 同时CAP处理30 s后钙化结节面积无显著变化。以上结果表明, 本试验条件下的CAP处理可抑制hUC-MSCs的增殖, 但对其体外成骨分化无明显影响。
大气压冷等离子体 间充质干细胞 细胞增殖 成骨分化 cold atmospheric plasma mesenchymal stem cells cell proliferation osteogenic differentiation
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Electronic Thin Films and Integrated Devices, School of Optoelectronic Information, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
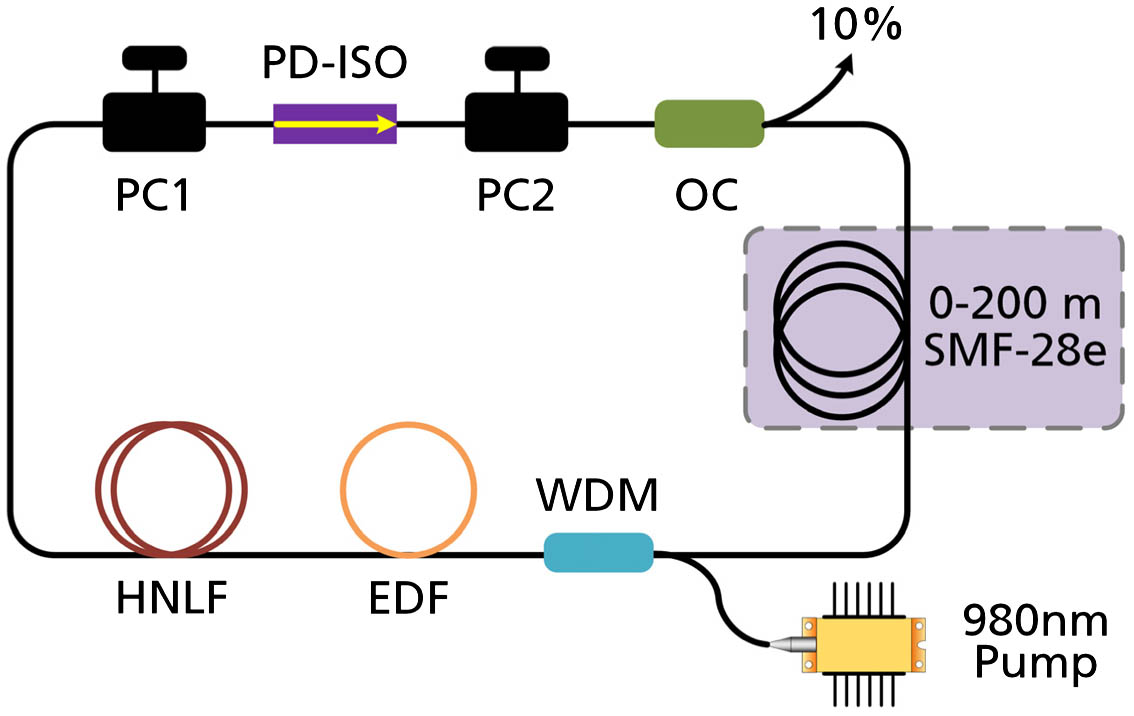
The pulse dynamics of harmonic mode-locking in a dissipative soliton resonance (DSR) region in an erbium-doped fiber ring laser is investigated at different values of anomalous dispersion. The fiber laser is mode-locked by a nonlinear polarization rotation technique. By inserting 0–200 m anomalous dispersion single-mode fiber in the laser cavity, the cavity length is changed from 17.3 to 217.3 m, and the corresponding dispersion of the cavity ranges from ?0.27 to ?4.67 ps2. The observed results show that the tuning range of repetition rate under a harmonic DSR condition is highly influenced by the cavity dispersion. Furthermore, it is found that, by automatically adjusting their harmonic orders, the lasers can work at certain values of repetition rate, which are independent of the cavity length and dispersion. The pulses at the same repetition rate in different laser configurations have similar properties, demonstrating that each achievable repetition rate represents an operation regime of harmonic DSR lasers.
(060.4370) Nonlinear optics fibers (060.5530) Pulse propagation and temporal soliton (140.3510) Lasers fiber (140.4050) Mode-locked lasers. Photonics Research
2017, 5(6): 06000612

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Electronic Thin Films and Integrated Devices, School of Optoelectronic Information, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
We report an erbium-doped fiber laser passively Q-switched by a few-layer molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) saturable absorber (SA). The few-layer MoS2 is grown by the chemical vapor deposition method and transferred onto the end-face of a fiber connector to form a fiber-compatible MoS2 SA. The laser cavity is constructed by using a three-port optical circulator and a fiber Bragg grating (FBG) as the two end-mirrors. Stable Q-switched pulses are obtained with a pulse duration of 1.92 μs at 1560.5 nm. By increasing the pump power from 42 to 204 mW, the pulse repetition rate can be widely changed from 28.6 to 114.8 kHz. Passive Q-switching operations with discrete lasing wavelengths ranging from 1529.8 to 1570.1 nm are also investigated by using FBGs with different central wavelengths. This work demonstrates that few-layer MoS2 can serve as a promising SA for wideband-tunable Q-switching laser operation.
Lasers, Q-switched Lasers, erbium Nanomaterials Photonics Research
2015, 3(3): 03000A92
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Electronic Thin Films and Integrated Devices, School of Optoelectronic Information, University of Electronic Science & Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
A novel method for accurately measuring chromatic dispersion of optical fibers is proposed based on the use of chirped intensity-modulated signals. Unlike the conventional method, the proposed method utilizes the configurable transfer function of optical fibers caused by the residual chirp of intensity modulation, which not only eliminates the chirp error but also improves the measurement range through adjusting the chirp parameter of the intensity modulator. Our method is applicable for measuring both the magnitude and sign of chromatic dispersion of optical fibers or other dispersive devices at different operating wavelengths by using a vector network analyzer.
Radio frequency photonics Fiber measurements Dispersion Chirping Photonics Research
2014, 2(4): 04000B26





